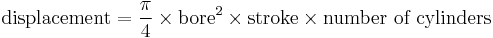Engine displacement
Engine displacement is the volume swept by all the pistons inside the cylinders of an internal combustion engine in a single movement from top dead centre (TDC) to bottom dead centre (BDC). It is commonly specified in cubic centimeters (cc), litres (l), or (mainly in North America) cubic inches (CID). Engine displacement does not include the total volume of the combustion chamber.
Contents |
Definition
Engine displacement is determined from the bore and stroke of an engine's cylinders. The bore is the diameter of the circular chambers cut into the cylinder block.
Examples: The 427 Chevy bore is 4.312 in, and the stroke is 3.65 in, therefore the displacement for this 8-cylinder engine is:
- 3.1416/4 * 4.3122 * 3.65 * 8 = 426.41380142592 CID.
If the bore is 10 cm and the stroke is 5 cm with 4 cylinders, the calculation is:
- 3.1416/4 * 102 * 5 * 4 = 1570 cm3 = 1.57 liters
Units of measure
In the United States, the cubic inch was the commonly used unit of measurement until the 1980s by the manufacturers to express the displacement of engines for cars, trucks, etc. (e.g., the "426" in 426 HEMI refers to 426 cubic inches displaced). It is still used for this purpose in the context of the classic-car hobby, auto racing, and so forth.
The automotive industry nowadays uses the International System of Units / le Système international d'unités (SI), a modern metric system for this purpose worldwide (e.g. 6.1 litre HEMI). However, in markets accustomed to cubic inches, the actual displacement measurements of an engine are still given by many manufacturers in these units, usually along with metric value; e.g. the 6.1 litre HEMI's published displacement is 370.0 CID/6,059 cc.[1][2][3][4] Some examples of common CID-to-litre conversions are given below. Note that nominal sizes are not always precisely equal to actual sizes. This principle is frequently seen in engineering, tool standardization, etc. (for ease of use) and in marketing (when a big round number sounds more impressive, is more memorable, etc.).
| make (± division) | cubic inch displacement (CID) - (actual) (nearest 1) |
cubic inch displacement (CID) - (nominal) |
International System of Units (SI) - (actual) (nearest 0.01) |
International System of Units (SI) - (nominal) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Honda, Kawasaki, others | something close to 61 CID | N/A (not marketed in CID) | [something close to SI nominal] | 1000 cc (= 1.0 litre) |
| Honda, Kawasaki, others | something close to 98 CID | N/A (not marketed in CID) | [something close to SI nominal] | 1600 cc (= 1.6 litre) |
| Honda, Kawasaki, others; Ford | something close to 122 CID | N/A (not marketed in CID) | [something close to SI nominal] | 2000 cc (= 2.0 litre) |
| GM (Pontiac, Buick, Oldsmobile, GMC, others) | 151 CID | N/A (not marketed in CID) | [something close to SI nominal] | 2.5 litre |
| Toyota, Ford, Chrysler, others | something close to 183 CID | N/A (not marketed in CID) | [something close to SI nominal] | 3.0 litre |
| AMC, Jeep, Chrysler (I6) | 241.573 CID | 242 CID | 3,959 cc | 4.0 litre |
| Ford | something close to 244 CID | N/A (not marketed in CID) | [something close to SI nominal] | 4.0 litre |
| Ford (Ford, Mercury), GM (Chevrolet, GMC) | [something close to CID nominal] | 250 CID | 4.10 litre | 4.1 litre |
| AMC, Jeep, International Harvester | [something close to CID nominal] | 258 CID | 4.22 litre | 4.2 litre |
| GM (Chevrolet, GMC, Oldsmobile) | [something close to CID nominal] | 262 CID | 4.33 litre | 4.3 litre |
| Ford (Ford, Mercury) | [something close to CID nominal] | 289 CID | 4.74 litre | N/A (not marketed in SI) |
| Ford (Ford trucks and vans) | [something close to CID nominal] | 300 CID | 4.92 litre | 4.9 litre |
| GM (Pontiac) | [something close to CID nominal] | 301 CID | 4.9 litre | N/A (not marketed in SI) |
| Ford, GM (Chevrolet) | [something close to CID nominal] | 302 CID (302 Windsor, 302 Cleveland, Chevrolet 302) | 4.95 litre | 5.0 litre |
| GM (Oldsmobile) | 303 CID | |||
| AMC, Jeep, International Harvester | [something close to CID nominal] | 304 CID | 4.98 litre | 5.0 litre |
| GM (Chevrolet, Pontiac, Oldsmobile, Buick) | [something close to CID nominal] | 305 CID | 5.0 litre | N/A (not marketed in S/I) |
| GM (Chevrolet; Buick) | 307 CID | 307 CID | 5.03 litre | N/A (not marketed in SI) |
| GM (Oldsmobile) | 307 CID | N/A (not marketed in CID) | 5.03 litre | 5.0 litre |
| Chrysler (Chrysler, Dodge, Plymouth) | [something close to CID nominal] | 318 CID | 5.21 litre | 5.2 litre |
| AMC, GM (Chevrolet) | 327 CID | 327 CID | 5.36 litre | N/A (not marketed in SI) |
| GM (Oldsmobile) | 330 CID | |||
| Buick, Chrysler (Chrysler, Dodge, Plymouth) | [something close to CID nominal] | 340 CID | 5.57 litre | N/A (not marketed in SI) |
| GM (GMC, Chevrolet, Buick, Oldsmobile, Pontiac, others) | [something close to CID nominal] | 350 CID | 5.74 litre | 5.7 litre |
| Ford (Ford, Mercury) | [something close to CID nominal] | 351 CID (Cleveland or Windsor) | 5.75 litre | 5.8 litre |
| AMC, Chrysler (Chrysler, Dodge, Plymouth) | [something close to CID nominal] | 360 CID | 5.90 litre | 5.9 litre |
| Chrysler (Chrysler, Dodge, Plymouth) | [something close to CID nominal] | 383 CID | 6.28 litre | N/A (not marketed in SI) |
| GM (Pontiac) | [something close to CID nominal] | 389 CID | 6.5 litre | N/A (not marketed in SI) |
| AMC, Ford, GM (Cadillac) | [something close to CID nominal] | 390 CID | 6.39 litre | N/A (not marketed in SI) |
| GM (Oldsmobile) | 394 CID | |||
| GM (Chevrolet) | [sometimes 396 CID, sometimes 402 CID] | 396 CID | 6.49 litre | N/A (not marketed in SI) |
| GM (Chevrolet, Pontiac, Oldsmobile) | [something close to CID nominal] | 400 CID | 6.55 litre | N/A (not marketed in SI) |
| GM (Buick) | 401 CID | |||
| GM (Chevrolet) | [something close to CID nominal] | 409 CID | 6.70 litre | N/A (not marketed in SI) |
| GM (Pontiac) | [something close to CID nominal] | 421 CID | 6.90 litre | N/A (not marketed in SI) |
| GM (Oldsmobile) | 425 CID | |||
| Chrysler (Chrysler, Dodge, Plymouth) | [something close to CID nominal] | 426 CID (Wedge or Hemi) | 6.98 litre | 7.0 litre |
| Ford (Ford, Mercury) | [something close to CID nominal] | 427 CID | 7.00 litre | 7.0 litre |
| GM (Pontiac),Ford (Ford, Mercury) | [something close to CID nominal] | 428 CID | 7.01 litre | 7.0 litre |
| Ford (Ford, Mercury) | [something close to CID nominal] | 429 CID | 7.03 litre | 7.0 litre |
| Chrysler (Chrysler, Dodge, Plymouth) | [something close to CID nominal] | 440 CID | 7.21 litre | 7.2 litre |
| GM (GMC, Chevrolet) | [something close to CID nominal] | 454 CID | 7.44 litre | 7.4 litre |
| GM (Buick, Oldsmobile, Pontiac) | [something close to CID nominal] | 455 CID | 7.46 litre | N/A (not marketed in SI) |
| Ford (Ford [trucks and vans]; Lincoln [cars]) | [something close to CID nominal] | 460 CID | 7.54 litre | 7.5 litre |
| GM (Cadillac) | [something close to CID nominal] | 472 CID | 7.73 litre | 7.7 litre |
| GM (Cadillac) | [something close to CID nominal] | 500 CID | 8.19 litre | 8.2 litre |
| Chrysler (Dodge) | 506.5 CID | 505 CID | 8285 cc | 8.3 litre |
| Chrysler (Dodge) | 509.8 CID | 510 CID | 8354 cc | 8.4 litre |
| GM (GM Performance Parts) | [something close to CID nominal] | 572 CID | 9373 cc | 9.4 litre |
Governmental regulations
Taxation of automobiles is sometimes based on engine displacement, rather than the actual power output. Displacement is a basic fundamental of engine design, whereas power output depends a great deal on other factors, particularly on how the car manufacturer has tuned the engine from new. This has encouraged the development of other methods to increase engine power, such as variable valve timing and turbochargers.
There are four major regulatory constraints for automobiles: the European, British, Japanese, and American. The method used in some European countries, and which predates the EU, has a level of taxation for engines over one 1.0 litre, and another at the level of about 1.6 litres. The British system of taxation depends upon vehicle emissions for cars registered after 1 March 2001, but for cars registered before this date, it depends on engine size. Cars under 1549 cc qualify for a cheaper rate of tax.[5]
The Japanese method is similar to the European taxation by classes of displacement, plus a vehicle weight tax.
The United States does not tax a vehicle based on the displacement of the engine (this is also true in Canada, Australia, and New Zealand). Engine displacement is important in determining whether or not smaller vehicles need to be registered with the state and whether or not a license is required to operate such a vehicle. A common threshold is 50cc.
In the Netherlands[6] and in Sweden, road tax is based on vehicle weight. However, Swedish cars registered in 2008, or later, are taxed based on carbon dioxide emissions.
Displacement is also used to distinguish categories of (heavier) and lighter motorbikes with respect to driving licence and insurance requirements. In France and some other EU countries, mopeds of less than 50 cm3 displacement (and usually with a two-stroke engine), can be driven with minimum qualifications (previously, they could be driven by any person over 14). This led to all light motorbikes having a displacement of about 49.9 cm3. Some people tuned the engine by increasing the cylinder bore, increasing displacement; such mopeds cannot be driven legally on public roads since they do no longer conform to the original specifications and may go faster than 45 km/h.
Wankel engines, due to the amount of power and emissions they create for their displacement, are generally taxed as 1.5 times their stated physical displacement (1.3 litres becomes effectively 2.0, 2.0 becomes effectively 3.0), although actual power outputs are far greater (the 1.3 litre 13B can produce power comparable to a 3.0 V6 engine, and the 2.0 litre 20B can produce power comparable to a 4.0 V8 engine). As such, racing regulations actually use a much higher conversion factor.
Automotive model names
In the automotive industry, engine displacement is frequently encoded in the auto manufacturer's model names. For instance, Nissan's Teana 350JM is a car with a 3498 cc (213.5 cubic inch displacement (CID))]] engine). Motorcycles are often labeled similarly. However, this can be misleading. For instance, the BMW 335i only has a 3.0 litre (twin-turbocharged) engine. Lexus hybrid vehicles (h) are marked higher than its engine size to signify the extra power from its auxiliary systems. (Examples: RX450h has a 3.5L engine, LS600h has a 5.0 engine)[7]
See also
References
- ^ "2008 Dodge Charger – specs & upgrades". Chrysler. http://www.dodge.com/bridge/vehsuite.html?app=vehiclespecs&family=charger&model=Technical&zipcode=90210&year=2008. Retrieved 2008-05-02.
- ^ "Ford Vehicles: get specifications F-150". Ford Motor Company. http://www.fordvehicles.com/trucks/f150/features/specs/. Retrieved 2008-04-25. "Engine type: 5.4L Triton SOHC 24-valve V8... Displacement (cu. in.): 330 CID"
- ^ "Chevrolet 2008 Silverado Pickup Truck - specifications (under engine 'tab')". GM. http://www.chevrolet.com/silverado/specifications/. Retrieved 2008-04-25. "Engine: Vortec 5.3L Aluminum-Block V8...Displacement (cu. in.): 325"
- ^ "Dodge specifications". Chrysler LLC. http://www.dodge.com/bridge/vehsuite.html?app=vehiclespecs&family=ram_2500&model=Technical&zipcode=48226&year=2008. Retrieved 2008-04-25. "Powertrain: Engine - Displacement - Cubic Inches: 345.0"
- ^ The Cost of Vehicle Tax for Cars, Motorcycles, Light Goods Vehicles and Trade Licences." Direct.gov.uk
- ^ Road tax also based on region and fuel type (petrol / CNG, LPG, Diesel, or other (electric/hybrid/H2))
- ^ https://www.press.bmwgroup.com/pressclub/p/pcgl/pressDetail.html?outputChannelId=6&id=T0084262EN&left_menu_item=node__2229